Main features of the digital signature
A digital signature is a unique characteristic in digital form, something like a fingerprint embedded in a document. The signer must have a digital certificate to be associated with the document.
The certification authority issues the digital signature.
It is comparable to a driver's license or passport. A digital certificate helps to verify the document's authenticity to determine if it has been tampered with. It plays a primary role in identity verification.
Another significant feature of a digital signature is that it is used for protecting digital documents. Fraudsters can forge documents to submit online using an electronic signature, but with a digital signature, it is nearly impossible. The electronic document is protected; only an authorized person can view it to make changes or edits.
When a digital signature is applied to a specific document, the digital certificate is bound to the signed data in a single, unique fingerprint. These two components of a digital signature are unique, and it makes them more practical than wet signatures because it is possible to authenticate their origin. This cryptographic operation helps to perform the following actions:
- Proving the authenticity of the document and its source
- Ensuring that there were no changes in the document after signing
- Confirming the identity of the signer.
Main features of an electronic signature
Under US law, an electronic signature is any electronic symbol, process, or sound associated with a record or contract that the interested party intends to sign. Thus, the main feature of an electronic signature is the intention to sign a document or agreement. Another noteworthy aspect that distinguishes an electronic signature from a digital signature is that an electronic signature can be oral, a simple mouse click, or any electronic authorization.
The main characteristic of an electronic signature is that it reveals the signer's intent to sign the document. It usually complies with contracts or other agreements that are entered into by two parties. As mentioned earlier, there are different types of electronic signatures. They are legally binding once all parties have demonstrated their commitment and intention to enter into a particular contract.
Another aspect of an electronic signature is that it helps to verify the authenticity of the document.
Once it has been signed, the parties involved should be able to be identified. However, an electronic document can be hard to verify because there is no digital certificate, making the process secure.
Another notable feature of an electronic signature is that it is used to execute an agreement. For example, in a contract, two people usually agree to perform certain obligations. This agreement becomes legally binding if both parties sign it. In this case, you can use an electronic signature. In addition, electronic signatures are often used in contracts because they are easy to use.
Table Showing Differences between Digital Signature and Electronic Signature
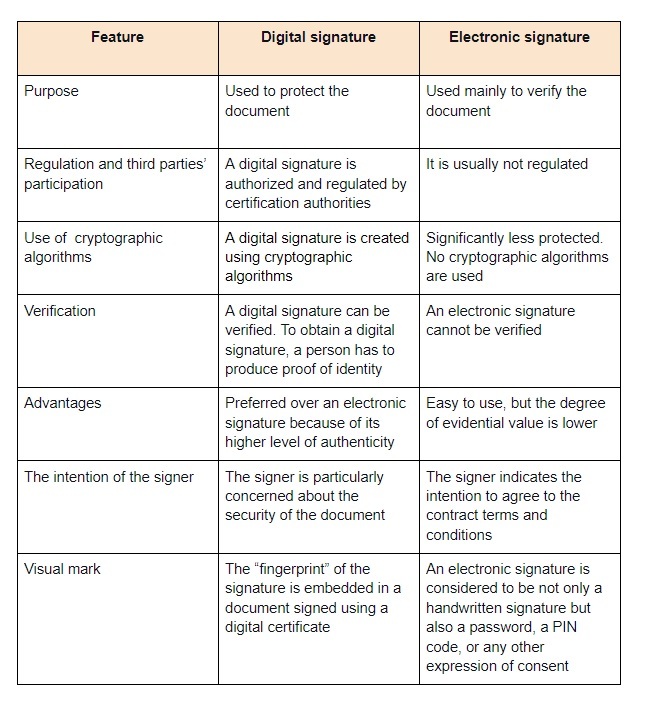
Thus, although both electronic and digital signatures are legally binding, it is preferable to use the latter because they are more secure than the former.
Conclusion
Digital signatures and electronic signatures are different in some very significant ways. We have tried to give a brief overview of the types, having highlighted their main differences. Knowing what types of signatures an organization needs to collect impacts the technology and processes you need to implement.
The original resource used for this article can be foundhere. If you find our posts compelling, you can subscribehere; we will be delighted to get feedback.